Half-rack configurations
Whereas there is no formal specification for "half rack", the term half-rack can have different separate meanings: It can describe equipment that fits in a certain number of rack units, but occupy only half the width of a 19-inch rack (9.5 inches (241.30 mm)). These are commonly used when a piece of equipment does not require full rack width, but may require more than 1U of height.[citation needed] For example, a "4U half-rack" DVCAM deck occupies 4U (7 in) height × 9.5 in width, and in theory, two 4U half-rack decks could be mounted side by side and occupy the 4U space. It can also describe a unit that is 1U high and half the depth of a 4-post rack (such as a network switch, router, KVM switch, or server), such that two units can be mounted in 1U of space (one mounted at the front of the rack and one at the rear). When used to describe the rack enclosure itself, the term "half-rack" typically means a rack enclosure that is half the height (22U tall). There is also a "half rack width" size being used in IT applications where a device conforms to a smaller than 9.5-inch width so that these "half rack width" appliances may be used in a chassis system that fits the traditional 19-inch rack space, but allows for these 8.4-inch-wide "half rack width" appliances to be inserted and removed easily without tools or the need to remove adjacent hardware. This "half rack width" concept is popular in applications where IT equipment is being used by military who are unable to use traditional 1U full-depth IT appliances due to their large size.
Dari Wikikamus bahasa Indonesia, kamus bebas
PK ! sæ{ î ppt/presentation.xmlì˜ÑnÛ †ï'í,ßN© Ø�Õ™Òm™&uRµt@m’XÃ`éÒN{÷±¢iÒnsÌø9şPàÛ÷û–ÏDȆ³27qVñºa›2üş¸œäa f5¦œ‘2|!2|?û涛u‚HÂVzh m˜œá2Ü*ÕÍ¢HV[ÒbyÃ;´¶æ¢ÅJ?ŠMTüSÛ·4‚qœE-nXØ�ÿ2�¯×ME>òj×êé&‚P›‡Ü6�ܺqsßbœ’ÄÏdµ{’D-9SRÓ çúµ%¿b©ˆøRßKuÖ4uB�L“e‰f'f¦G+ Œæ·Ñ¥áŒ+"ÿÖw2A°w¹4F;�Û‡d2àdaÇ»r2Jùráȉ'gSGN=ºæ™/»æSONcGÎ=¹/Vø£]ľ]İ.Ïعº.é>¹4qué>;”¹º¹ğÀz©«ûø—.¸ÀÏ�^àç.=ôù¥îÚC�*Fş?TŒü=~¨ù{üPáò�>¿Ø}èó‹GÿŸ_6Êßç]şÈã§n~È)îŸxõTû2,€^.“põR†Y�æöA½tº"ËJÂ’}OĞV†~Ø1Òɉ@S�] Tz@©(‡¹Íş ÈPée'@æ™İ®€•ĞÔ4MеF©ô€ò CçZ¤�Tz@…(K§×"}¤bO²ş³›év¶Õ`'š2üõi¹XŞA„&q†–“Ş¥“\oz“âã-Sp· ñâ·¹yƒÔœˆ?ïššh“á�Rï–ß6•à’¯ÕMÅÛşsAÔñŸDt¼±_ <Üñ®ciåzI¸hÓô·\¼†AÇ¥¹Ïg†µ ¨]})6OGÊ‹d�ö~ClËú�OS½iı‡©m;8,r uøºÜÏó? ÿÿ PK ! îLIü M# ! ppt/slideMasters/slideMaster1.xmlìZ]n7~/Ğ;,öµ�Wû¿,–¥œÔˆô™Ú¥¤¹?àR²œ¢@ïĞô}ëQz’‡¤µ�~ì N;zñ�†ßgæãIÉÇ/V³–”7yUl÷¨k[´L«,/gûÃ帓ØV#H™V•t`ßĞÆ~qòıwÇu¿aÙ[ÒÊ-°Q6}2°çBÔ}ÇiÒ9-HsTÕ´„±iÅ"à#Ÿ9'×`»`�×íFNAòÒÖïó‡¼_M§yJ_Vé¢ ¥PF8eD€ÿÍ<¯c~ˆµšÓÌàÛw\:�øÒ–Éçd¦ş�ó“cÒŸ°¼çŒYY�lH¯ÄϹ˜_ÌI ùqm²xŸš lş&s}Ô³Eáœ; OßÓT8(NE:—â&Ğz§5 _”ÓK�NsÖ Ìxˆ‚t¸©/9¥R*—¯y}QËQˆêİòœ[y&]µJR€Ï¶£4?–KœO^Ÿ‘ôWS^È'Pb07ò/ÆBWÂJ•2]kÓùO[°éüÕ´c&pZ“ʨ”s›áôL8—0ù°ZYÉm\l‰(eÔámo ,JâÈ#t9 ’�£�u��Ça(çı¨çûŞ�H¿æ�xM«Â’, ×YjöÖ©.+I±rO9U÷¥ûÙ ..xB<לÀ/¡*a 6ª˜Ì.¤út!À„¶¬ğ¸üq!nEïqı¡šƒ5FdÁÓ²óᶲœäA�ÎY^^�X�^ÁŠ–‰–Ë9ĞreXœ\__ц,ÊÙlÁ�Hz”gr\(f«ÌÎ 'ïwN¦ó€Q›h1úa–3¤²¦%kÁ¡{‘7J†�¡Œ;ÁË^Ü9GagúA0&§#ÿÕo²ªİ ŸrŠÿ&3 6šE‘§¼jª©8J«Bw§®®)¯«�ÛÕİkI ó^7 }/êvUfĞ7óDo�uCIKjk2s6P†bRvÒdæI�'u�Ô�DÒz ´`4�ÑÜb|£ñ�&0šÀhB£ �&2XâH6$C>lkZ±•ÂHªx óŸ‘›j!Şdš‰–‹Ñsƒ8Hü(€ª\¯š�·ï`ä…Å Úƒ•�×`ı{°n‹ôìÁz-lxÖoa£{°A߃�ZXİÄvb㶷µsæb½í·á"s²7ˆ+ì( ʹ`?b³Y2Wö]Âfp²H‡R§ÓK2¹øÍÚ ‚®ôG`ײ(9+‡ü 7%¹™—ú#Í¡YÀ‰á|Q¦Âì¯M�éTKç©P5hZÈzt²xıÛÌ-[O“«©¯(—'Øó•ÉŠå™ÙY±ĞãÊ0Ô§1İF¡£–¸©é”¤°ñüPüÒaBï ä“Jôn×|2�6Ú¶òE�;Õ [Y±™o¤¸ üs•—Ô1Šÿ]Ú!ƒİm©W¥hÅzÊsÂl«Îá(3&EÎäf)7Í9á E§1AÛ9““|gĞ]ÆY¹‹³rgå~ÎPôÖ¼Ä�דıÊ�Óñ’0– E{z�@ƒê�ıÏï(m›«äKÕ×#r% Ò\ùk®\7ğq¥Éò’H*�Yn’õÅšá#’%Òd-²€éñs%kKe}nü?È’i²Â5Y^7Œ‘€gIÖß=M®$Aš«¨ÅUèHÍ·ÓŸY’!MVÜ"«»¸áÈúšÈ’i²’5Y>œ¿±óÅS K2¤ÉêµÈJ’è9Ÿ/�(Y’!õ=÷ú.\÷+1§üöfoœ+Jutí¯o�jÈÆ5úñémåX5ë¯<ÇÛo²Ac=ò³ıöh’pÈÏ�›Ë;Û!A».Inâ%èı!A;n&¸´û6ş¡Gï;�ƒ»‡&½ïÔ…ñ¡Iß=i¶—øë´ùÑKı&¦ş æä_ ÿÿ PK ! =vû=v 9 ppt/slides/slide1.xmlìXKoÛ8¾/Ğÿ@èîèı°Q§ˆíxlÓQ‚�i‰¶„P—¤gûßwHJqì8mÒ¤‡6M ñ5Î73œ¡çı‡MEÑšpQ6õĞr�‘:kò²^«Ëi/±��¸Î1mj2´n‰°>¿ûã=š#Ø]‹Z…”l`Û"+H…ÅQÃH k‹†WXÂ�/íœãàZQÛsœÈ®pY[í~ş”ıÍbQfdÒd«ŠÔÒ0á„b ’‹¢d¢ãÆ�Â�q"€�޽#Ò1 ËRš«V°KNˆêÕë?9KÙŒëåOëGeú²P�+P‹e·-™Ökݱ÷¶/».l¼R-`C›¡Ê¿U_[Í‘�D™™Ì¶³Yñù mVœ ¶»ì{‡*TF¸‡p¼Îe))AîªN^Á>6Ùµ@ux|ï�Â`V-+�¼eÀ*“\skIͺîlå9¨/r¼Ä‰4LÏ�ûIï*&rƒ0 c8 'ööQÖl 7£&¿U›çĞj«à2•·”èÓЦK¸Ô¥åâ0K±º¤î]¥pşZ>xŒ…ò’KmD8WúĞ|Á©j�~�3ĞÀ /1µÃu#`èxÎȉœ Úî?€ÕRfÅW%~>Ldæ‚ȉÅ+³´52ÅZO8VcifŸ…ü'EŒ¾ïOné/JÉË·físôV ~~”î[›Ôùs|ñËÙ{L™Î]ì×éàëùÏïò_ºšK�uFyi «¹I�pÈf»å©°ŸÄ‰èT臱ï¸Ñn*£$‰|Ϥ l$/L…�_/ø"Bzš�¡pçb|�Çw/&eŠY‹†æ„#ÿ5
Dari Wikikamus bahasa Indonesia, kamus bebas
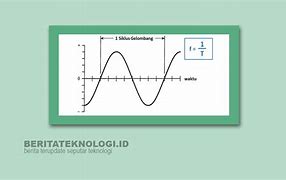
Secara fisik, Komputer terdiri dari beberapa komponen yang merupakan suatu sistem. Sistem adalah komponen-komponen yang saling bekerja sama membentuk suatu kesatuan. Apabila salah satu komponen tidak berfungsi, akan mengakibatkan tidak berfungsinya suatu komputer dengan baik. Komponen komputer ini termasuk dalam kategori elemen perangkat keras (hardware). Berdasarkan fungsinya, perangkat keras komputer...
Periferal (unit tambahan)
Periferal (unit tambahan)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The hasta (Sanskrit: हस्त (hásta); Chinese: 肘 (pinyin: zhǒu)) is a traditional Indian unit of length, measured from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It equals 24 aṅgulas orᅠ about 18 inches,[1] about 45 centimetres.
4 hastas make one dhanus,[2] and 400 hastas make one nalva. 8 hastas make one rajju.
Bacaan 1: Yer 17:5-8Bacaan 2: 1Kor 15:12. 16-20Injil: Luk 6:17. 20-26
MEMBAHAS si miskin dan si kaya selalu menarik. Dunia pun terpolarisasi oleh hal ini, baik secara person maupun negara. Ada orang miskin dan negara miskin demikian juga sebaliknya.
Dalam Alkitab, ada beberapa perikop yang membahas tentang hal ini. Misalnya, Lukas 6: 17-26 dan Matius 5:1-12.
Permenunganku dari kedua perikop ini ada dua:
Maka saya ingin merenungkan secara total. Baik miskin secara rohani maupun materi. Baik miskin secara rohani maupun materi.
“Miskin” untuk menggambarkan ketidakberdayaan seseorang.
Tidak ada orang miskin punya kuasa. Dalam kelemahannya, ia lebih mudah untuk berserah diri kepada yang berkuasa, yaitu Allah.
Dibandingkan dengan si kaya, yang lebih cenderung sombong dan merasa bisa melakukan apapun dengan kekayaannya. Bahkan mungkin ia mampu melupakan Tuhan yang telah memberinya kekayaan.
Menjadi kaya tentu saja tidak salah, namun bagaimana mengelola kekayaan itu yang lebih penting.
Ada empat penghiburan bagi orang lemah dalam perikop ini:
Dalam kelemahannya, ia lebih mudah menerima iman dibanding mereka yang memiliki kekuatan (kekayaan). Lebih mudah percaya, lalu menyerahkan dirinya secara total dan terakhir taat dalam melaksanakan kehendak-Nya.
Hal ini, secara tegas telah difirmankan Allah jauh hari dalam Yeremia:
“Terkutuklah orang yang mengandalkan manusia, yang mengandalkan kekuatannya sendiri, dan yang hatinya menjauh dari pada TUHAN… Diberkatilah orang yang mengandalkan TUHAN, yang menaruh harapannya pada TUHAN.”
Dalam pengajarannya kepada jemaat Korintus, Paulus mendapatkan pertentangan tentang ajaran “Kebangkitan Badan”.
Korintus masih dalam pengaruh Yunani, termasuk dalam iman. Ada kelompok yang menolak ajaran kebangkitan, termasuk jemaat Korintus.
Mereka dibaptis, mengaku mengimani Kristus, namun menolak ajaran kebangkitan yang merupakan puncak iman dalam keselamatan.
Paulus meyakini bahwa:
“Kristus telah dibangkitkan dari antara orang mati, sebagai yang sulung dari orang-orang yang telah meninggal.”
Jemaat Korintus banyak terdiri orang-orang kaya, namun sepertinya masih miskin dalam iman.
Kekayaan adalah berkat dari Tuhan, dan tidak salah menjadi kaya. Namun jangan sombong merasa paling kuat.
“Jadilah seperti lilin, yang tidak pernah menyesal saat nyala api membakarmu. Tetaplah pakai maskermu dan jaga jarakmu.”
Unit of measure for electronic equipment
A rack unit (abbreviated U or RU) is a unit of measure defined as 1+3⁄4 inches (44.45 mm).[1][2] It is most frequently used as a measurement of the overall height of 19-inch and 23-inch rack frames, as well as the height of equipment that mounts in these frames, whereby the height of the frame or equipment is expressed as multiples of rack units. For example, a typical full-size rack cage is 42U high, while equipment is typically 1U, 2U, 3U, or 4U high.
The rack unit size is based on a standard rack specification as defined in EIA-310. The Eurocard specifies a standard rack unit as the unit of height; it also defines a similar unit, horizontal pitch (HP), used to measure the width of rack-mounted equipment. The standard was adopted worldwide as IEC 60297 Mechanical structures for electronic equipment – Dimensions of mechanical structures of the 482.6 mm (19 in) series, and defines the sizes for rack, subrack (a shelf-like chassis in which cards can be inserted), and the pitch of printed circuit boards/cards providing physical compatibility of technological equipment, typically in telecommunications.[citation needed]
While a rack unit is defined as 1+3⁄4 inches (44.45 mm), a front panel or filler panel in a rack is not an exact multiple of this height. To allow space between adjacent rack-mounted components, a panel is 1⁄32 inches (0.03125 in or 0.794 mm) less in height than the full number of rack units would imply. Thus, a 1U front panel would be 123⁄32 inches (1.71875 in or 43.66 mm) tall. If n is number of rack units, the ideal formula for panel height is h = (1.75n − 0.031) for calculating in inches, and h = (44.45n − 0.794) for calculating in millimetres. Manufacturing allows for dimensions with less precision.
The 19-inch rack format with rack units of 1.75 inches (44.45 mm) was established as a standard by AT&T around 1922 in order to reduce the space required for repeater and termination equipment in a telephone company central office.[3]
A typical full-size rack is 42U,[4] which means it holds just over 6 feet (180 cm) of equipment, and a typical "half-height" rack is 18–22U, which is around 3 feet (91 cm) high.
The mounting-hole distance (as shown to the right) differs for 19-inch racks and 23-inch racks: 19-inch racks use uneven spacings (as shown to the right) while 23-inch racks use evenly spaced mounting holes. Although it is called a 19-inch rack unit, the actual mounting dimensions of a 19-inch rack unit are 185⁄16 inches (18.3125 in or 465.1 mm)[5] wide, center to center.
Rack units are universally the same, but the type of thread[6] can vary depending on the rack. Mounting rails can be No. 10-32 tapped (Unified Thread Standard), No. 12-24 tapped, metric M6 threaded or universal square holes. Universal square holes are becoming the most common as these allow the insertion of replaceable cage nuts for the type of thread needed.[citation needed] This prevents stripping of the threading on the rails and allows for more flexibility.























